Jobghost.blogspot.com explains most important topics in Civil engineering for the GATE-2016 examination. Here the “TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING-Highway Materials and testing” topics are explained. The important test and test procedures in civil engineering are mentioned. Each and every word given below is important for all your civil engineering competitive examinations. And also the GATE-2016 practice sets, Example problems, previous year Question papers are available in jobghost.blogspot.com.
Subgrade is the
foundation or earth fill which directly bear the loads from the pavement. This
layer lies just below the pavement. It should provide adequate support to the pavement.
And it should not get affected due to adverse climate and loading conditions.
Modulus of Sub-grade reaction (K):
It is the pressure
sustained per unit deformation of subgrade at specified deformation or pressure
level, in plate bearing test. So it is the behavior of subgrade for the
specified pressure. The modulus of subgrade reaction found out by using
subgrade reaction test. Standard dimensions of the tests given below.
Standard plate size for test = 75 cm
Standard Settlement = 0.125 cm
Standard Pressure = 0.7 kg/ cm2
Formula for K:
There are two methods
available to find the modulus of sub-grade reaction.
i.
In this
method the standard settlement value taken as constant and the load causes the
standard settlement is taken as test pressure “p”. Then the sub-grade reaction value is..
ii.
In this
method the standard pressure is taken as constant and settlement due to the
standard load is taken as the test settlement value. Then the subgrade reaction
value is ..
P -----> Pressure in kg/
cm2
Plate Correction for
Different plate used for test:
The subgrade modulation
test always performed with 75cm diameter standard plate. But sometimes due to
the site conditions various size diameters are used. To rectify the error due
to change in diameter, following formula is used.
k1-----> K @ Smaller plate
a1---->
Radius of smaller plate
K ----> K for
Standard plate
a ----> Radius of standard
plate
2.
CBR
Test:
This test is used for
evaluating the stability of soil subgrade and other flexible pavements.
Flexible pavement thickness is determined based on this test. Usually this test
is conducted in the laboratory and also in the field.
It is an arbitrary
strength test and hence cannot be used to evaluate the soil properties like
cohesion or internal friction or shearing resistance. Material passing 20 mm
sieve is only used. The presence of coarse grained particles would result in
poor results in the test. The test is meant for soil but it is also carried out
on sub base and granular base course materials.
The test apparatus
consists of Cylindrical mould of diameter 150 mm , Base plate , Cylindrical
plunger of 50 mm diameter and compression testing machine.
Test procedure:
Test specimen is kept
in a mould and it is subjected to four days soaking. Then the load is applied
in the cylindrical plunger of 5cm diameter so that the penetration rate is 1.25
mm/minute. The load penetration curve is plotted for all penetration values.
The test load for 2.5 mm and 5 mm penetration are recorded.
The CBR value found out with the following two formulas.
The CBR value found out with the following two formulas.
CBR value for 2.5 mm
penetration
CBR value for 5.0 mm
penetration
* Standard load
@ 2.5 mm penetration = 1370
* Standard load @ 5 mm
penetration = 2055
* Higher of Two value taken as CBR value.
* Normally CBR (2.5) value is always greater than the CBR (5.0).
i.e[CBR(2.5) > CBR (5)]
3. Marshal
Stability test for Bitumen:
Marshall Stability test
is to determine the stability of bitumen at 600 standard test temperatures.
Stability is defined as the load carrying capacity of compacted specimen at
test temperature. So this test is conducted to find the load carrying capacity
of paving bitumen at high temperature. Tis test is applicable to hot-mix paving
mixture containing 2.5cm size aggregates.
It is the type of
Unconfined compressive strength test , in which a cylindrical specimen 10 cm
diameter and 6.3 cm height is compressed radially at a constant rate of strain
of 5 cm/minute.
Standard temperature 60oC
the corresponding load carrying capacity of specimen is called marshal
stability value and the deformation at failure in units of 0.25 mm is recorded
as Marshal Flow value. Prior to stability density voids analysis is carried out
on the test specimens. The optimum binder content for the aggregate mixture and
anticipated traffic conditions is a compromise value which meets specified
requirements for stability flow value and voids content.
Voids In Mineral
Aggregate:
Voids In Mineral Aggregate(VMA) = Va + Vb
Volume of air voids
Volume of bitumen
Theoretical Specific Gravity
Gm= Measured specific gravity
Voids
Filled With Bitumen:
Here…
ca=Coarse aggregate
|
fa=fine aggregate
|
fill
=filler
|
bit =bitumen
|
Gt ----> Theoretical Specific
Gravity
Gm ----> Measured Specific Gravity
W ----> Weight
G ----> Specific Gravity
Va ---->Volume of
air voids
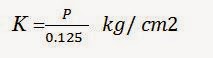








No comments:
Post a Comment